Note about vaccines: If you are at risk of exposure and would like a vaccine, you can view upcoming Mpox vaccination clinics and/or register to be notified when vaccines are available in your area.
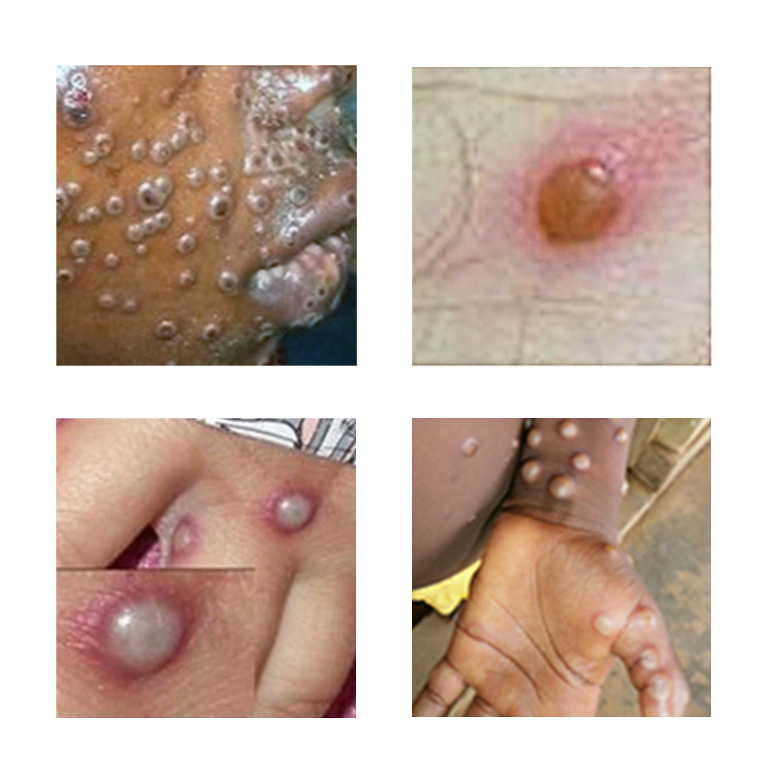
Mpox virus (MPXV) belongs to the Orthopoxvirus genus in the family Poxviridae. The Orthopoxvirus genus also includes variola virus, the virus that causes smallpox, among others. Mpox is not related to chickenpox.
Mpox was first discovered in 1958 when two outbreaks of a pox-like disease occurred in colonies of monkeys kept for research, hence the name "Mpox." The first human case of Mpox was recorded in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo during a period of intensified effort to eliminate smallpox.
The natural reservoir of Mpox remains unknown. However, African rodents and non-human primates may harbor the virus and infect people.
There are two main clades of the virus, Congo and West African, with distinct genetic variations. The mortality rate is not well-defined but may be about 10% for the Congo clade and less than 1% for the West African.
The current global 2022 outbreak has been sequenced and is related to the less severe West African clade.